Introduction
This guide is intended to provide some easy to follow steps for your wireless equipment installation. Read it over to prepare, and use it to keep track of tasks on installation day.
Following you will find sections on:
- Wireless node preparation
- Site preparation
- Wireless node installation
- Clean-up, testing and post-installation tasks
Review of these materials should only take about an hour, though if you are using it in a classroom or instructional setting, it may take longer. Keep in mind this is a broad overview of all the steps required to install rooftop equipment. Each step along the way will take time - in fact, rooftop installations may take anywhere between two and six hours, depending on site conditions and equipment.
Installations normally take between 1 to 5 hours, depending on the complexity.
Materials + Supplies Needed
- The router or routers you plan on installing
- Mounting equipment and hardware
- The installation site plan
- Ethernet cables
- The power supply for your routers, usually a Power over Ethernet adapter.
- Tools for installation
Wireless Router Preparation

This guide is intended to provide some easy-to-follow steps for your wireless equipment installation. It is especially helpful to keep track of tasks the day you are planning on working, but we recommend you read it over beforehand in order to best prepare.
The first step is to get the wireless equipment and install your custom firmware, if you are planning on using one. For more information on using custom firmware, see the What in the world is a firmware? and Installing a new firmware documents. You can do this on the day of the install, or in the days leading up to it. If your neighborhood network has particular settings for the network, make sure to get those as well before installing the software.
- Acquire the routers that are compatible with your custom firmware and appropriate for the location.
- Download the custom firmware images you need for your hardware. Again, you can consult Installing a new firmware for links to alternate firmware images. If you are planning on using the firmware that came with the routers, you can skip this step.
- Install and configure the router using the settings appropriate to your network, and for the site.
- Keep a record of the router’s mesh or network IP address after it is configured. This can help you access and troubleshoot the device after it is connected to the network.
- Also record the router’s MAC address - this is a unique ID that you can use to keep track of the hardware, in case you need service from the manufacturer.
To find the MAC address for your router, look on the bottom label or inside the bottom cover of the router for a code that looks like “aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff”. That is the MAC address. It is a unique combination of numbers and letters that identifies the specific device.
Finding the mesh IP address will be different depending on the custom firmware you are using. Consult the documentation!

You can write the node’s name on the case with a permanent marker, or a printed label if you have a label maker.
Site Preparation
It is a good idea to visit the site where you plan on installing a new wireless node a few days or a week before the actual installation. This allows more time to prepare and acquire any missing equipment or hardware.

- Do some site assessments. Using the guidelines and examples in Inventory the Neighborhood to survey buildings and sites for wireless installations. The document includes a set of questions and things to look for, and is a good place to start.
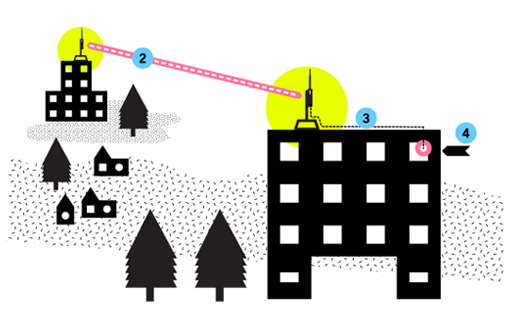
- Pick the best mounting location on the roof based on visibility to other rooftops. Keep in mind wireless signals work best when there is a clear line of sight between the nodes. Also figure out what kind of mount you will use to install. The document Learn about Rooftop Mounts can help you decide.
- Identify where the Ethernet cable will run along the roof and enter the building.
- Identify where the Power over Ethernet (PoE) adapter will plug in.
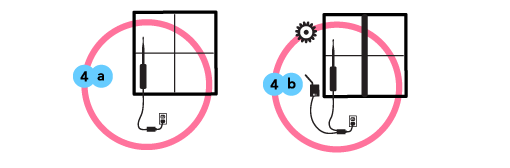
(Option A) If the node is mounted in an enclosure or indoors, try to find an accessible location that keeps it out of the way from everyday interaction.
(Option B) If the building owner or node host wants to donate bandwidth to make the node an Internet gateway, put the PoE adapter where it can plug into the host’s router easily.
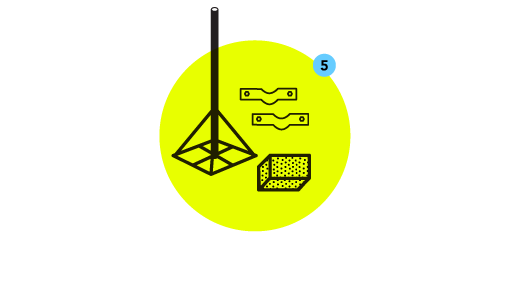
- Acquire the proper mounting hardware.
The document Learn about Rooftop Mounts can help you identify the right hardware. There are many places to find mounting hardware - your local hardware or electronics store may have some, but there are various vendors online as well.
Check that you have all the necessary hardware for mounting, such as concrete anchors, bolts, clamps, etc.
- Verify that the tool bag has everything you need for the mounting hardware and installation site.
Wireless Router Installation

Installation day! Now you get to go up on the roof and install new equipment for the community network - but make sure you are working in a safe and responsible way. We recommend going through Learn Rooftop Basics document and reviewing some rooftop safety guidelines before you start your installation.
You can break the job into three parts: installing the mounting hardware; installing the node and power supply; and running the Ethernet cable between the node and power supply.
- Install the mounting hardware. This will vary depending on the type of mount you are using. If it came as a kit, read and follow the installation instructions! For more information, refer to the Learn about Rooftop Mounts document.
For an eaves or anchor mount kit, drill the holes necessary for the anchors. Make sure to use outdoor rated anchors (plastic or metal).
For a chimney mount kit, make sure the strap is extremely tight!
For a non-penetrating roof mount, make sure to use at least a few concrete blocks (4” thick blocks are enough - you don’t need full 8” thick blocks).
- Attach the wireless node to the mounted mast. Use metal hose clamps or heavy-duty outdoor rated plastic zip-ties if possible. This will keep the wireless node from slipping or twisting off the mast.
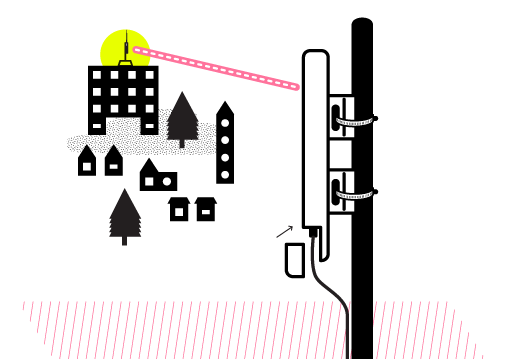
If possible, face the indicator lights on the node towards the street or ground, so they are visible without climbing onto the roof. This can help with troubleshooting in the future.
If you are using a directional node, point it directly to where it should link to another node.
Plug in the Ethernet connector into the node and close the housing.
Plug in the Power over Ethernet (PoE) adapter and secure it in some way, so it isn’t hanging by the power plug. Zip-ties or a wall-mounted enclosure may help with this.
- Run the Ethernet cable between the wireless node and the Power over Ethernet adapter.
Follow the tips in the “Learn Rooftop Basics” module for how to run the Ethernet cable, and how to secure it to the mast, walls and on roof surfaces.
Make sure the Ethernet cable is secured in such a way that the cable cannot be stepped on, and will not whip around in the wind during a storm.
- Install the RJ45 connectors on the Ethernet cable ends. Each end should be wired identically, using the proper color code for the wire order (known as T568B). Then plug the cable into the Node and PoE adapter, and you are finished with the installation steps.
Clean up, Testing and Post-Installation
No installation is finished unless you leave the site looking better than when you arrived. Never leave a mess! Make sure you have not left any unsealed holes in the building exterior where water may enter.
1. Clean up the rooftop and PoE location.
Cut off any loose or extending ends from zip-ties.
Clean up any wire or cable pieces.
Ensure service loops in the cable are secured in some way.
Sweep away mortar dust / wood dust if you did any drilling.
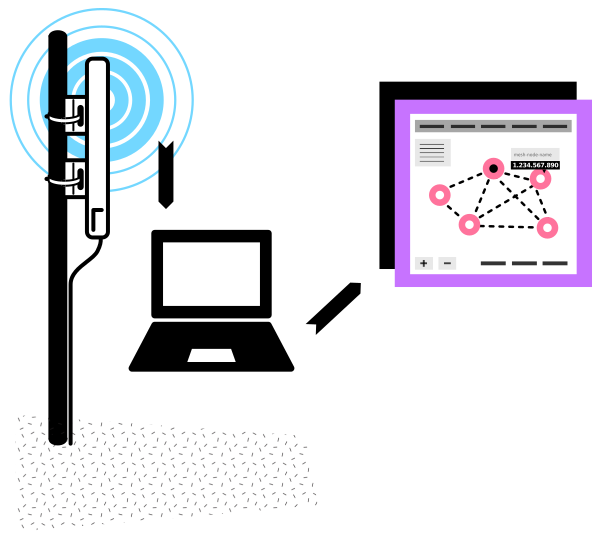
2. Check connectivity to the wireless node.
After a couple of minutes, associate with the Access Point (AP) on your phone or a laptop. Confirm that you can connect.
Bring up the wireless node’s Administration page.
Navigate to the OLSR status page that shows you neighbor nodes on the mesh, if there are any. Confirm that this node is connected to others.
If there is an Internet Gateway on your network, check that you can get out to the Internet.
3. Record any necessary information about the installation in your network’s documentation.
For example, in addition to the node name, MAC address, and IP address, make a note of the location and what worked and did not work, as well as any follow-up or next steps.
Definitions
- MAC Address
- A unique combination of numbers and letters that identifies a specific device.
- IP Address
- A unique string of numbers separated by periods that identifies each device attached to a network.
- Line of Sight
- An unobstructed path for wireless signals to travel between buildings or devices.
Related Information
Other documents referenced in this one:


